The Hubble Space Telescope: What are its greatest hits? | Science & Tech News
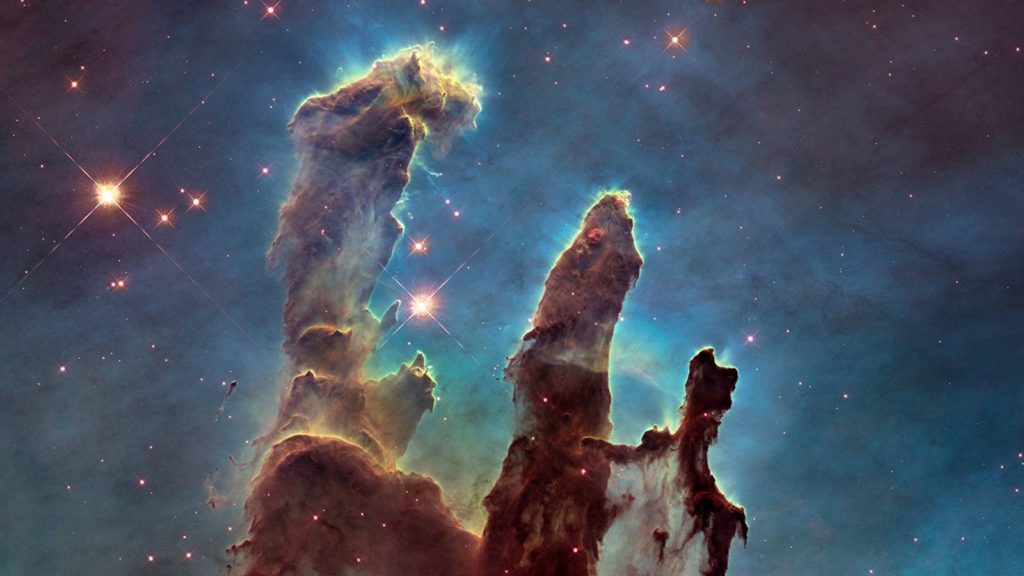

Few human inventions have had as much of an impact on our scientific understanding of the universe and our cultural imagination as the Hubble Space Telescope.
Later today the first set of images from NASA’s new James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will usher in a generation of images of deep space that will expand our minds in just the same way.
But before we enjoy the fruits of the JWST, let’s have a re-cap of some of Hubble’s greatest successes.
History of Hubble
The space telescope was named after the American astronomer Edwin Hubble who is celebrated for observing that all of the other galaxies we can see in the universe seem to be moving away from us.
Data collected by the Hubble Space Telescope helped uncover evidence that not only was the universe expanding – it was actually accelerating.
While the cause of that acceleration is currently unknown, it earned three of the researchers who discovered it – Saul Perlmutter, Brian Schmidt and Adam Riess – the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics.
The space telescope has also given us a profound sense of perspective and its colourised images have been an inspiration for much of the space-travel scenes in the Marvel Cinematic Universe.
Hubble Deep Field image
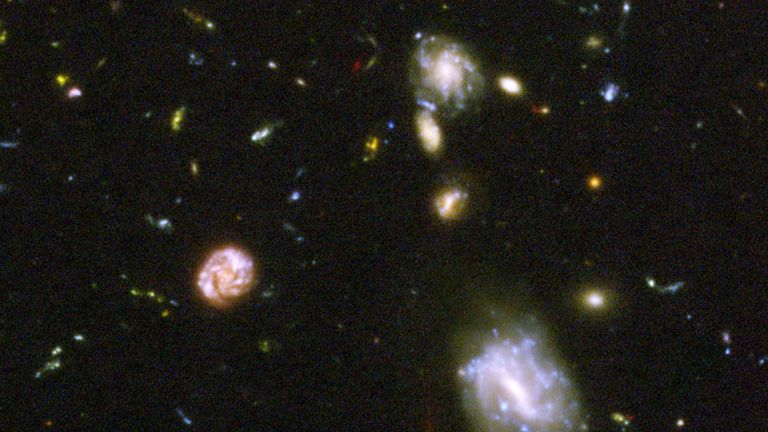

This was the previous deepest view of the universe humanity had ever captured
The famous Hubble Deep Field image – a long exposure of a tiny and apparently empty slice of the night sky – revealed thousands of distinct galaxies, potentially all of them as complicated and distinct as our own.
The first JWST image – released yesterday by the President of the United States – was also a deep field shot.
It is the farthest humanity has ever seen in both time and distance, closer to the dawn of time and the edge of the universe, with part of the image showing light from soon after the Big Bang.
Hubble has also uncovered proto-planetary discs in the Orion Nebula where planets are beginning to form, but its age has taken a toll.
Back in 2018 it had to be put into safe mode when two of the telescope’s four gyroscopes failed. Although a fix was found, eventually Hubble will be decommissioned.
Hubble’s discoveries
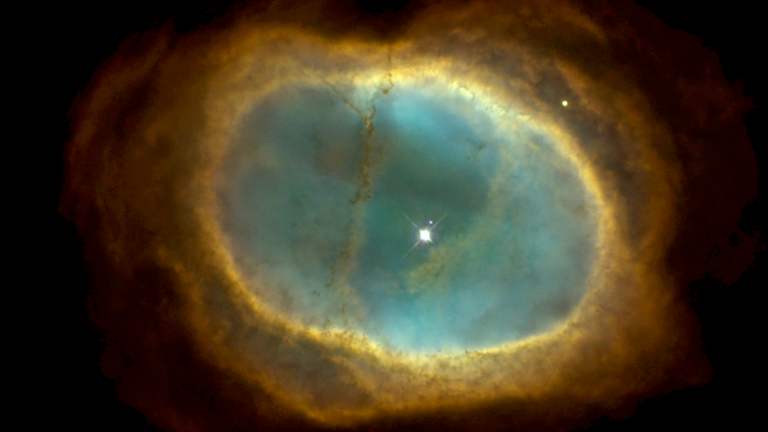
Hubble caught this arresting image of planetary nebula NGC 3132
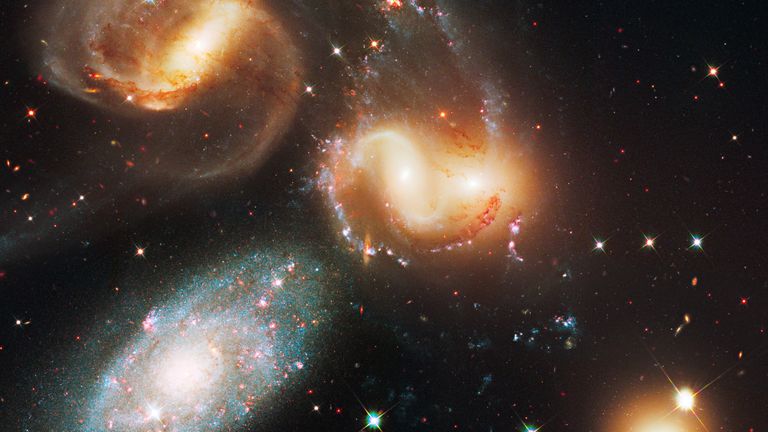

Hubble imaged the galaxy group known as Stephan’s Quintet located in the constellation Pegasus
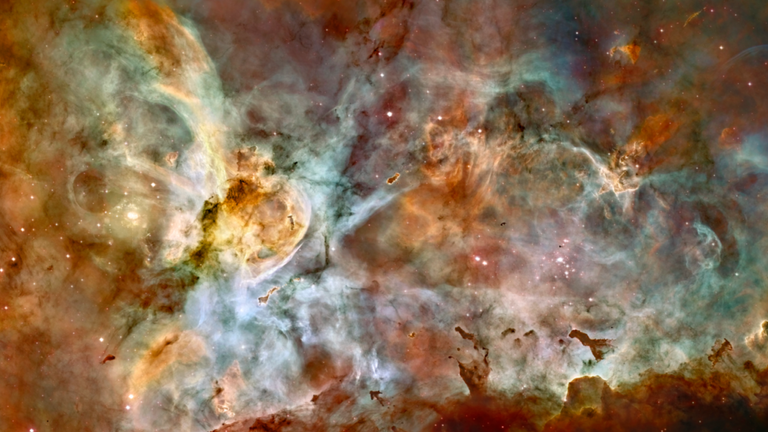

Hubble imaged this 50-light-year-wide view of the central region of the Carina Nebula
Its data has been cited in thousands of peer-reviewed papers published in academic journals, and these papers have been referenced in more than 600,000 others – a cascading effect showing the enormous impact that the space telescope has had on our understanding of the universe.
NASA states that this total increases by roughly 150 every day.
Hubble is one of the largest astronomy tools ever put into space. It has been orbiting the Earth since 1990 at an altitude of around 540km, capturing some of the most captivating images of deep space humanity has ever seen.
Capturing ‘Einstein Rings’
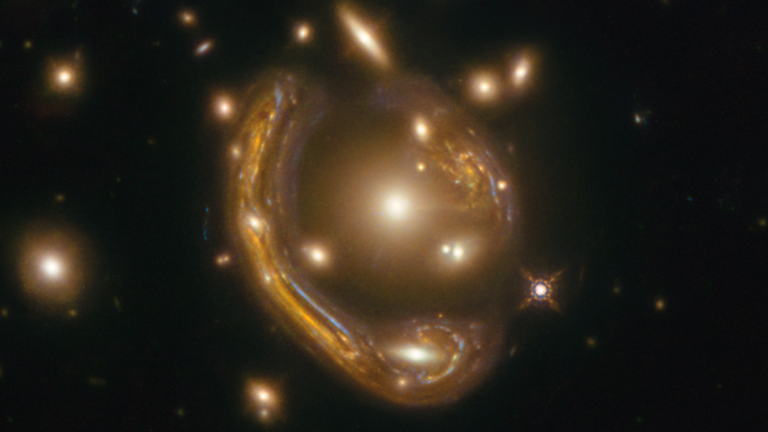
Einstein Ring. Pic: Saurabh Jha (Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey)
Back in December 2020 it captured an image of one of the most complete “Einstein Rings” ever seen, a phenomenon theorised by the great scientist in his general theory of relativity – and now scientists have published their research into what it was that they were looking at.
A year earlier it discovered a quasar with the brightness of about 600 trillion suns – the brightest ever seen in the early universe.
Its work has been essential to proving the relationship between the mass of black holes at the centre of galaxies and the properties of those galaxies themselves.
Analysis: NASA reveals picture of distant universe taken by James Webb Space Telescope – but why is it a big deal?
Spotting a mysterious dark storm on Neptune
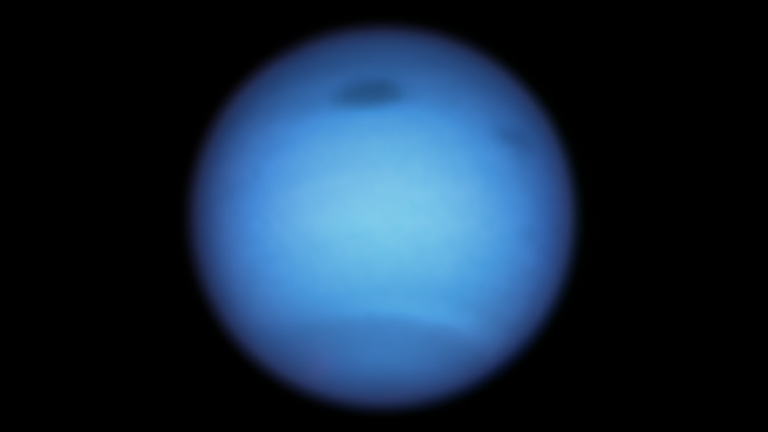
Hubble spotted this storm on Neptune suddenly reversing direction. Pic: NASA
At times its discoveries have baffled scientists. Back in 2020 it spotted a mysterious dark storm on Neptune abruptly reversing its direction, something they say has never been observed before.
The storm, which is wider than the Atlantic Ocean, had been raging in the gas giant’s northern hemisphere since at least 2018, and was slowly drifting towards the planet’s equator where such storms are expected to dissipate.
But instead of going gently to its death, and to the surprise of observers, the vortex suddenly changed direction and doubled back to the north. With so many discoveries under its belt, perhaps Hubble might also surprise us as it faces being replaced by the JWST.

Recent Comments